Note
Click here to download the full example code
Blind source separation using Picard and Picard-O¶
The example runs the Picard algorithm proposed in:
Pierre Ablin, Jean-Francois Cardoso, Alexandre Gramfort “Faster independent component analysis by preconditioning with Hessian approximations” IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018 https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.08171
and Picard-O algorithm proposed in:
Pierre Ablin, Jean-François Cardoso, Alexandre Gramfort “Faster ICA under orthogonal constraint” ICASSP, 2018 https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.10873
# Author: Pierre Ablin <pierre.ablin@inria.fr>
# Alexandre Gramfort <alexandre.gramfort@inria.fr>
# License: BSD 3 clause
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from picard import picard
print(__doc__)
Generate sample data
np.random.seed(0)
n_samples = 2000
time = np.linspace(0, 8, n_samples)
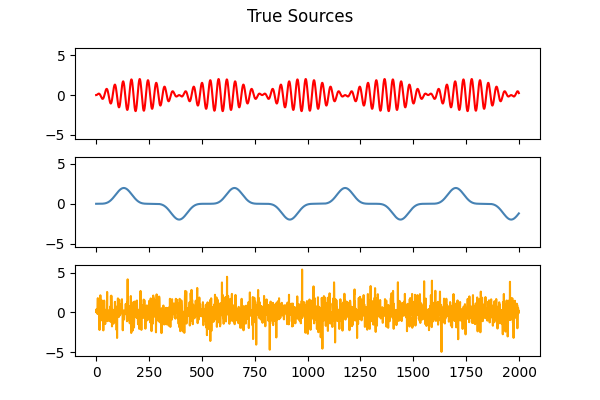
s1 = np.sin(2 * time) * np.sin(40 * time)
s2 = np.sin(3 * time) ** 5
s3 = np.random.laplace(size=s1.shape)
S = np.c_[s1, s2, s3].T
S /= S.std(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis] # Standardize data
# Mix data
A = np.array([[1, 1, 1], [0.5, 2, 1.0], [1.5, 1.0, 2.0]]) # Mixing matrix
X = np.dot(A, S) # Generate observations
# Compute ICA
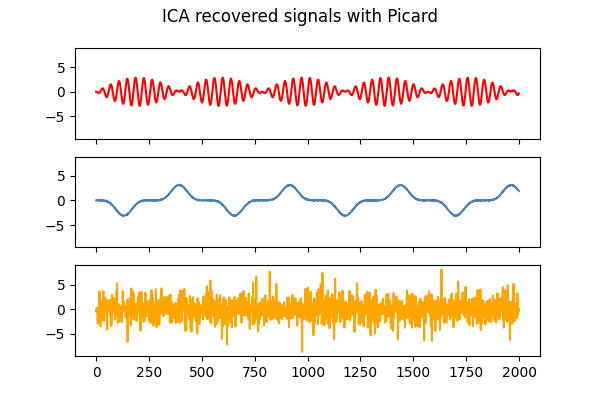
_, _, Y_picard = picard(X, ortho=False, random_state=0)
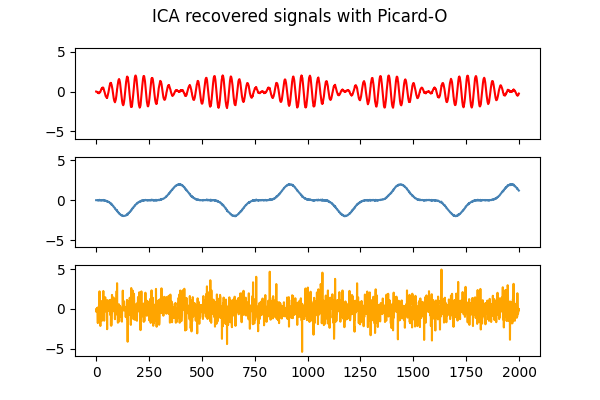
_, _, Y_picardo = picard(X, ortho=True, random_state=0)
Plot results
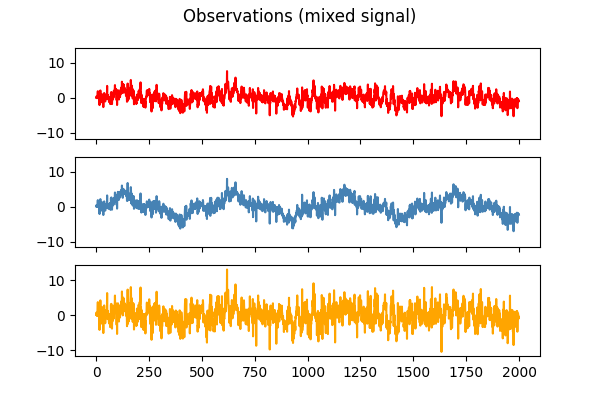
models = [X, S, Y_picard, Y_picardo]
names = ['Observations (mixed signal)',
'True Sources',
'ICA recovered signals with Picard',
'ICA recovered signals with Picard-O']
colors = ['red', 'steelblue', 'orange']
for ii, (model, name) in enumerate(zip(models, names), 1):
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 1, figsize=(6, 4), sharex=True, sharey=True)
plt.suptitle(name)
for ax, sig, color in zip(axes, model, colors):
ax.plot(sig, color=color)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 0.615 seconds)